As expectant parents, the journey of pregnancy is filled with excitement, anticipation, and a touch of nervousness. Amidst all this, prenatal testing plays a crucial role in ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. One such groundbreaking advancement in prenatal screening is Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT). Let’s dive into the details and explore what lies beyond the hype.
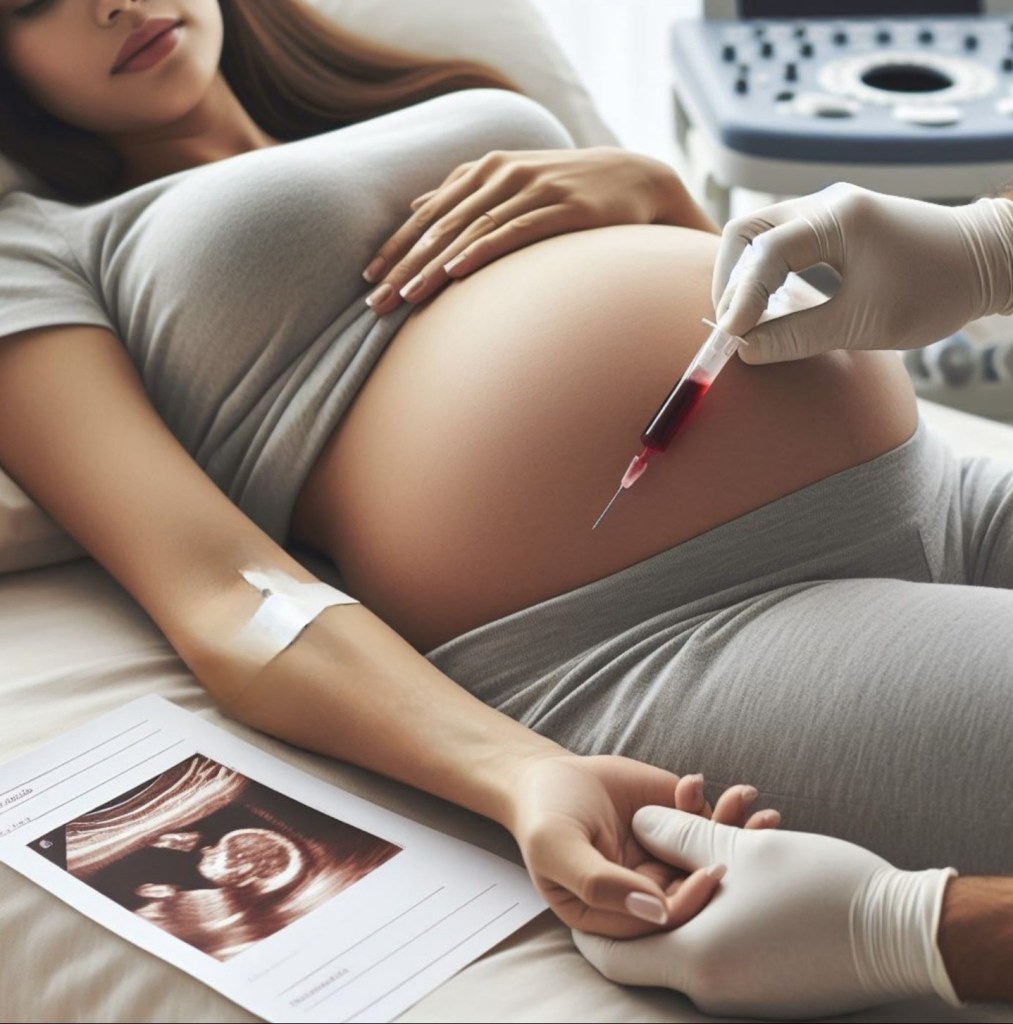
What Is NIPT?
NIPT, also known as cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) analysis, is a noninvasive method for assessing the risk of specific chromosomal anomalies during pregnancy. Unlike invasive procedures (such as amniocentesis), NIPT involves a simple blood draw from the pregnant person. The test analyses fragments of fetal DNA present in the maternal bloodstream, providing valuable insights into the baby’s genetic health.
When Is NIPT Ordered?
- Clinical Indications:
- NIPT is commonly ordered for the following reasons:
- Advanced Maternal Age: Pregnant individuals aged 35 or older
- Maternal Serum Screening Abnormalities: Unusual results from traditional blood tests
- Thickened Nuchal Translucency: Detected during ultrasound.
- Twin Pregnancies or pregnancies resulting from in vitro fertilization (IVF-ET).
- It also provides evidence for other abnormal karyotypes and copy number variations.
- NIPT is commonly ordered for the following reasons:
- Timing:
- NIPT can be performed as early as 10 weeks into pregnancy.
- It remains available until late pregnancy
Accuracy and Significance
- NIPT demonstrates exceptional accuracy for detecting specific chromosomal conditions:
- Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome): Extremely sensitive and specific.
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome): Also highly sensitive.
- Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome): Detectable with reliability.
- Sex Chromosome Abnormalities: Including Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome.
Clinical Significance
- NIPT aids decision-making by assessing the likelihood of fetal chromosomal abnormalities.
- It guides further diagnostic testing if needed.
- The concentration of cffDNA correlates with gestational age and test specificity.
Cost and Availability in India
- NIPT costs vary based on the testing facility and parameters considered.
- Approximate ranges: ₹10,000 to ₹20,000.
Limitations of NIPT
- Limited scope:
- NIPT primarily focuses on detecting specific chromosomal abnormalities and some microdeletion syndromes.
- It may not identify other genetic conditions or birth defects, which means it cannot replace a comprehensive ultrasound examination or other diagnostic tests entirely.
- Not diagnostic:
- NIPT is a screening test, not a diagnostic test. This means that it can only indicate the probability of having a chromosomal abnormality, but it cannot confirm or rule out the diagnosis.
- In cases of positive or unclear results, further diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, are usually recommended for confirmation
- False positives and false negatives:
- NIPT is highly accurate, but not 100% accurate. There is a small chance that NIPT may give a false positive result or a false negative result.
- The accuracy of NIPT depends on several factors, such as the quality and quantity of cffDNA, the gestational age, the maternal weight, and the laboratory methods.
Beyond the Hype
NIPT is more than just a buzzword; it’s a powerful tool that empowers parents with knowledge. As you embark on this remarkable journey, remember that NIPT provides a glimpse into your baby’s genetic makeup. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the ideal timing and make informed choices for a healthy pregnancy.
Remember, every baby is unique, and every parent’s journey is extraordinary. 🌟👶
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
